An execution management system plays a central role in modern trading by helping firms execute trades efficiently across increasingly fragmented and fast-moving markets. Execution management systems form part of a broader trading technology stack used in investment management, alongside other systems with distinct responsibilities such as order management systems (OMS) and portfolio management systems (PMS).
As trading strategies become more sophisticated and market structures more complex, execution management has evolved into a distinct discipline within professional trading infrastructure. Understanding how an execution management system functions—and how it differs from other management systems—is essential for firms seeking to improve execution quality, control trading costs, and manage operational risk.
This article provides an overview of what an execution management system is, how it works, and why it has become essential for traders, investment firms, and hedge funds operating across multiple asset classes.
What is an execution management system?
An execution management system is a specialized trading platform designed to support the trade execution phase of the trading process. Its primary purpose is to help traders access liquidity, route orders, and execute trades quickly while minimizing market impact and transaction costs.
Within the investment management technology stack, different systems serve different functions. Execution Management Systems (EMS) focus on execution, Order Management Systems (OMS) manage the full order lifecycle, and Portfolio Management Systems (PMS) support portfolio construction, monitoring, and analysis. Each system addresses specific workflows and user groups within an investment firm.
Unlike order management systems, which emphasize order tracking, allocation, and compliance across the entire lifecycle, an execution management system EMS is optimized for speed, precision, and decision-making at the point of execution. EMS platforms provide traders with real-time market data, advanced execution tools, and transaction cost analysis, enabling informed decisions in rapidly changing market conditions.
The role of execution management in modern trading
Execution management exists to address a fundamental challenge in trading: executing increasingly complex trades across markets that are fragmented among numerous venues, liquidity providers, and technologies.
Modern trading environments are characterized by multiple trading venues operating simultaneously, market conditions that can shift in milliseconds, and persistent pressure to achieve best execution while controlling trading costs. These dynamics make execution quality a critical determinant of trading performance.
Execution management systems provide the tools required to navigate this complexity. By combining market data, execution logic, and analytics within a single execution-focused system, traders gain the ability to respond quickly to market changes while managing market impact more effectively.
In addition, execution management supports the implementation of a wide range of trading strategies, from straightforward executions to more complex, multi-venue approaches, across different markets and asset classes.
Execution management vs order management systems
Execution management systems and order management systems serve distinct but complementary roles within trading infrastructure. Alongside these, portfolio management systems represent another key layer of the technology stack, each system supporting different functions and decision-makers.
Order management systems are designed to manage the full lifecycle of an order. They support portfolio managers, middle office functions, and compliance teams by handling order creation, allocation, tracking orders, reporting, and regulatory compliance. OMS platforms ensure that trading activity aligns with investment mandates and internal controls.
An execution management system, by contrast, is focused narrowly on execution. It provides traders with tools to route orders, access liquidity, and optimize execution quality in real time. While OMS platforms emphasize process, governance, and control, execution management emphasizes speed, precision, and interaction with trading venues.
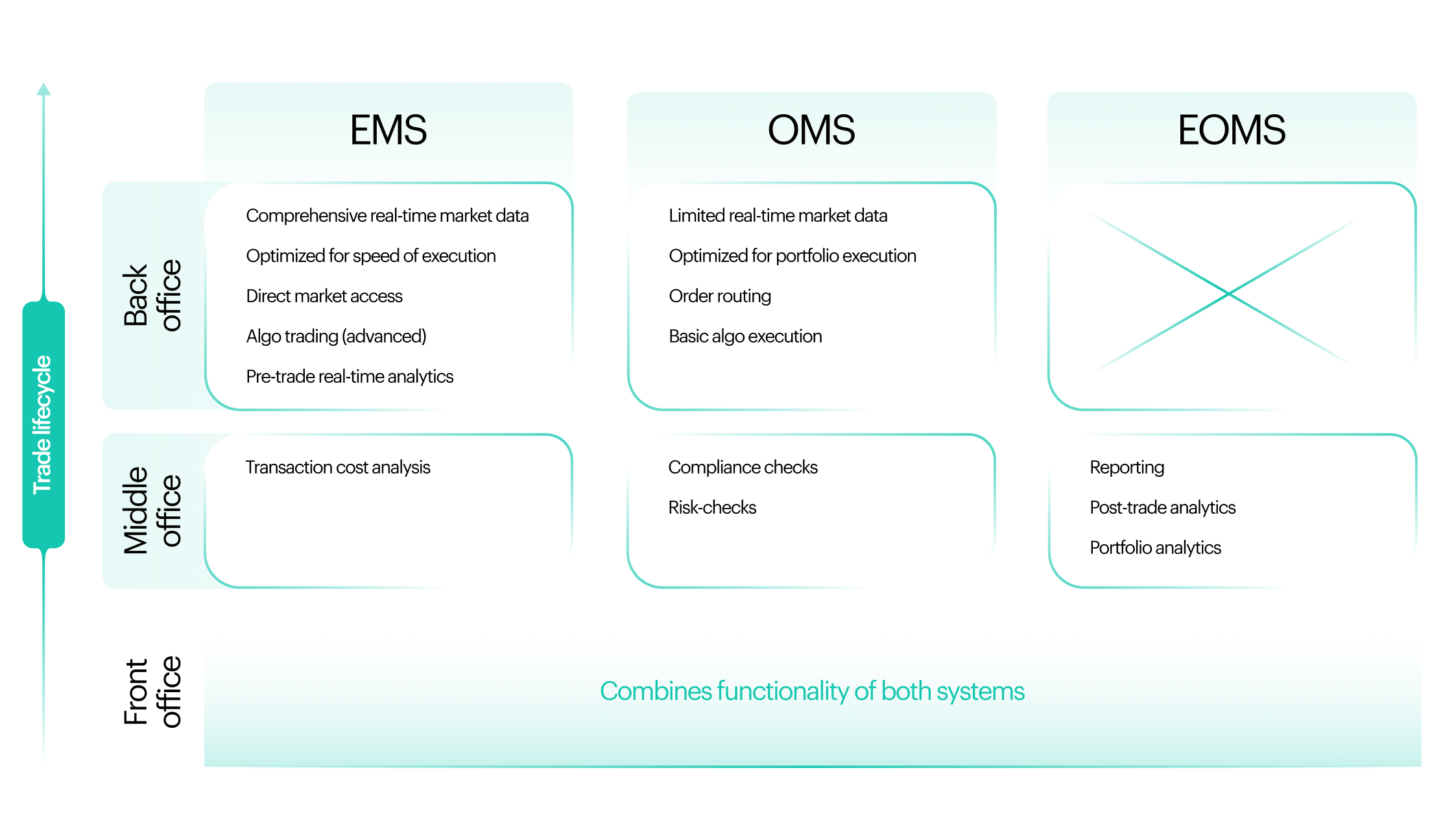
Many firms operate both systems simultaneously, while others adopt hybrid management systems that combine OMS and EMS functionality. Modern EMS platforms are designed to integrate easily with existing OMS and PMS environments, enabling seamless workflows across systems while preserving clear functional boundaries.
Core functionality of an execution management system
Execution management software is defined by a set of core capabilities that enable traders to execute trades efficiently in complex, fast-moving, and fragmented market environments. These capabilities are designed to support informed decision-making at the point of execution, where speed, precision, and control over market interaction are critical.
A well-designed execution management system brings together market data, execution logic, and analytics in a single workflow. This allows traders to manage execution quality consistently across asset classes, trading venues, and market conditions, while maintaining visibility into performance and costs.
Real time market data and analytics
Access to real time market data is foundational to effective execution management. Traders rely on live pricing, depth of market, and liquidity indicators to assess prevailing market conditions and determine how and where to execute trades.
Beyond raw price feeds, execution management systems aggregate and normalize data from multiple trading venues, enabling traders to compare liquidity and pricing across markets in real time. This consolidated view is essential in fragmented environments, where execution opportunities may differ materially from one venue to another.
Advanced analytics layered on top of real-time data allow traders to monitor execution quality as trades unfold, identify emerging liquidity patterns, and adjust execution tactics dynamically as market conditions change.
Order routing and access to trading venues
Execution management systems provide intelligent order routing that connects traders to multiple trading venues, exchanges, dealers, and liquidity providers. Rather than relying on static routing rules, modern EMS platforms use rules-based logic to determine the most effective execution path at any given moment.
Routing decisions can be tailored based on factors such as price, available liquidity, speed of execution, and anticipated market impact. This flexibility allows traders to adapt execution behavior to different trading strategies and market environments.
By providing direct access to a wide range of trading venues, execution management systems enable traders to source liquidity efficiently while maintaining control over where and how orders are executed.
Advanced execution tools and order types
Modern EMS platforms support a broad set of advanced execution tools designed to handle complex trades and sophisticated trading strategies. These include conditional orders, list trading, and multi leg orders, which allow traders to coordinate multiple executions within a single strategy.
Such tools are particularly important in markets where liquidity is fragmented or where large orders must be executed carefully to minimize market impact. By breaking trades into structured components or applying conditional logic, traders can manage execution risk more effectively.
Advanced execution tools reduce reliance on manual intervention, allowing traders to focus on strategy and execution oversight rather than operational mechanics.
Transaction cost analysis and performance measurement
Transaction cost analysis (TCA) is a core component of execution management, providing traders and firms with a structured way to evaluate execution quality and trading costs.
By applying cost analysis TCA, execution management systems measure factors such as slippage, timing costs, and market impact relative to benchmarks. These insights help traders understand how execution decisions affect performance and where inefficiencies may arise.
Over time, TCA supports continuous improvement in trading performance by informing refinements to routing logic, execution strategies, and venue selection. It also provides the data needed to demonstrate best execution and support internal governance and regulatory requirements.
Execution management systems across asset classes
Execution management systems are used across a wide range of asset classes, each with its own trading conventions, liquidity characteristics, and execution challenges. While the core objective of execution management remains consistent—achieving efficient trade execution with controlled cost and market impact—the way an EMS is applied can vary significantly depending on the market structure.
A robust execution management system must be flexible enough to adapt to these differences while providing a consistent execution workflow for traders operating across multiple markets. This adaptability is particularly important for firms managing diversified portfolios and executing across both listed and OTC environments.
Equities and listed markets
In equities and other listed markets, execution management focuses on speed, transparency, and adherence to best execution standards. Liquidity is typically centralized across electronic trading venues, but fragmented across multiple exchanges and alternative trading systems.
Traders interact with numerous brokers and electronic venues, making intelligent order routing a critical capability. Execution management systems help traders evaluate pricing and liquidity across venues in real time, enabling them to select the most effective execution path for each trade.
Market impact management is another key consideration in equities trading. Execution management tools allow traders to split large orders, apply algorithmic execution strategies, and monitor execution performance as trades progress, reducing adverse price movement while maintaining execution efficiency.
Fixed income and OTC markets
In fixed income and other OTC markets, execution management addresses a very different set of challenges. Liquidity is often fragmented, episodic, and less transparent, with pricing discovered through dealer interactions rather than centralized order books.
Execution management systems help traders source liquidity from multiple dealers and liquidity providers, consolidating pricing and availability information into a single execution workflow. This centralized view supports more informed execution decisions in markets where price discovery can be opaque.
Fixed income execution frequently involves more complex trades, larger notional sizes, and negotiation-based workflows. Execution management tools support these dynamics by enabling traders to manage quotes, compare execution options, and document execution decisions, helping control execution risk while maintaining auditability.
Multi-asset trading environments
Many investment firms operate in multi asset and multi market environments, executing across equities, fixed income, and other instruments simultaneously. In these contexts, a multi asset EMS provides a unified execution layer that allows traders to operate across asset classes within one system.
While execution logic differs by market, a multi-asset execution management system standardizes core workflows such as order routing, execution monitoring, and performance measurement. This consistency improves operational efficiency and reduces the complexity associated with managing multiple execution platforms.
By supporting execution across asset classes, a multi-asset EMS enables traders to implement a wide range of investment strategies, including pairs trading, basket execution, and program trades, while maintaining control over execution quality and risk across markets.
Who uses execution management systems?
Execution management systems are widely used by professional trading firms with complex and demanding execution requirements. These firms operate across fragmented markets, manage large volumes, and rely on technology to coordinate execution across multiple venues, liquidity sources, and trading strategies.
Execution management is relevant across both traditional financial markets and digital asset markets, where market fragmentation, venue diversity, and fast-changing liquidity conditions place similar demands on execution infrastructure. As a result, EMS adoption spans a broad range of market participants with different roles in the trading ecosystem.
In addition to buy-side institutions, sell side brokers use execution management systems to aggregate client orders, monitor execution quality, and improve the efficiency and consistency of trade processing across venues.
Hedge funds and proprietary trading firms
Hedge funds and proprietary trading firms are among the most advanced users of execution management systems. These firms rely on EMS platforms to support algorithmic trading, high-frequency strategies, and rapid responses to shifting market conditions.
Execution management is critical to maintaining performance in strategies where timing, routing decisions, and market impact directly affect outcomes. In both traditional markets and crypto markets, hedge funds operate across fragmented liquidity pools and multiple trading venues, making intelligent execution management essential.
Advanced EMS capabilities—such as algorithmic execution, smart order routing, and real-time monitoring—allow hedge funds to deploy custom strategies, adapt execution behavior dynamically, and control transaction costs while operating at scale.
Buy side firms and asset managers
Buy side firms and asset managers use execution management systems to implement trading strategies efficiently while maintaining oversight of execution quality and cost. For these firms, execution management serves as the interface between portfolio-level decisions and market execution.
Portfolio managers benefit from execution transparency and performance reporting, while traders use EMS tools to manage routing, liquidity access, and execution tactics. This separation of responsibilities is particularly important in institutional environments where governance and accountability are critical.
In markets such as digital assets, where liquidity and market structure can vary significantly across venues, execution management systems help buy-side firms maintain consistent execution standards while adapting to venue-specific dynamics.
Investment firms with complex trading strategies
Large investment firms executing across multiple asset classes and trading venues depend on execution management to coordinate trading workflows and manage operational risk. As trading strategies become more sophisticated, the need for centralized execution control increases.
Execution management systems enable these firms to standardize execution workflows across desks, markets, and instruments while preserving flexibility at the trader level. This balance is essential in environments that combine listed markets, OTC trading, and emerging asset classes.
By streamlining execution processes and integrating with other management systems, execution management supports scalable trading operations and reduces the risks associated with fragmented infrastructure.
Key benefits of an execution management system
The key benefits of execution management systems include:
-
More efficient trade execution
Centralized execution logic and direct access to multiple trading venues enable traders to execute trades quickly while maintaining control over how orders interact with the market.
-
Improved trading performance
Real-time visibility into prices, liquidity, and execution outcomes allows traders to adjust execution strategies dynamically as market conditions evolve.
-
Reduced transaction costs and trading costs
Intelligent order routing, access to diverse liquidity sources, and embedded transaction cost analysis help firms identify inefficiencies, reduce slippage, and optimize execution decisions over time.
-
Better control of market impact
Execution management systems provide tools to manage large or sensitive orders through order slicing, algorithmic execution, and continuous monitoring, limiting adverse price movement.
-
Enhanced ability to execute complex trades
Advanced execution tools and consistent workflows allow traders to manage multi-leg, list-based, and cross-venue trades with greater precision and lower operational risk.
These benefits are particularly important for firms operating in competitive, multi-venue trading environments, where execution quality, cost control, and speed are critical to overall trading outcomes.
EMS and trading strategies
Execution Management Systems have become a core component of institutional trading strategies. For investment firms and asset managers operating in volatile and fragmented markets, EMS platforms provide the execution layer that connects trading decisions with real-time market access.
By delivering real-time market data and direct connectivity to trading venues, an EMS allows traders to respond quickly as market conditions change. This capability is especially important for strategies executed across multiple asset classes, where liquidity can shift rapidly and execution timing directly affects outcomes and transaction costs.
Modern EMS platforms support a broad range of execution techniques, including conditional orders, list trading, and multi-leg execution strategies. These capabilities allow traders to manage complex trades within a structured framework, reducing reliance on manual coordination while maintaining control over execution logic.
Seamless integration with order management systems and other components of the trading technology stack ensures that execution strategies operate within a cohesive workflow. Execution data flows automatically between systems, supporting internal controls, compliance processes, and operational efficiency without disrupting trading activity.
Embedded transaction cost analysis tools complete the execution loop by providing detailed insight into execution quality and trading costs. These analytics enable firms to refine execution strategies over time, demonstrate best execution, and maintain consistent performance while managing risk across the broader trading infrastructure.
Choosing an execution management system
Selecting an execution management system is a strategic decision that affects trading performance, operational efficiency, and risk management across the organization. Because execution management sits at the intersection of market access, trading strategy, and technology infrastructure, firms must evaluate potential solutions carefully against both current and future requirements.
A primary consideration is whether the execution management system can support the firm’s trading strategies and execution style. This includes assessing asset class coverage, support for complex trades, and the availability of execution tools such as algorithmic strategies, smart order routing, and real-time monitoring. For firms operating across multiple markets, the ability to support multi-asset and multi-market execution within a consistent workflow is especially important.
Technology integration is another critical factor. An effective EMS should integrate seamlessly with existing order management systems, portfolio management tools, and risk management platforms. Well-documented APIs and flexible connectivity reduce implementation complexity, help preserve existing workflows, and minimize operational disruption during deployment.
Firms must also consider market access and connectivity. The ability to connect to relevant trading venues, liquidity providers, and brokers directly influences execution quality and scalability. As trading volumes grow or market structures evolve, the EMS should be able to scale without compromising performance or stability.
Beyond functionality, vendor experience and support play an important role in long-term success. Execution management systems operate in dynamic market environments, and continuous product enhancement is essential to keep pace with regulatory changes, market structure evolution, and new execution requirements. Reliable vendor support ensures that firms can address operational issues promptly and adapt their execution infrastructure over time.
Choosing an execution management system is not just a technology decision but an infrastructure investment. A well-aligned EMS enables firms to execute efficiently, manage risk effectively, and maintain consistency across trading operations as markets and strategies continue to evolve.
Execution management as a discipline
Execution management has become a core discipline because markets leave little room for imprecision. Liquidity is fragmented, execution paths are multiple, and trading decisions are only as good as their implementation in the market.
An execution management system exists to solve this specific problem. It gives traders control over how orders are exposed to the market, how liquidity is accessed, and how execution outcomes are measured. While it operates alongside order and portfolio management systems, its responsibility is clearly defined: execution quality at the point where risk becomes real.
For firms trading across venues and asset classes, execution management is not about adding complexity—it is about reducing it. A well-designed EMS brings structure to execution workflows, enforces discipline under pressure, and provides the feedback needed to improve execution decisions over time. In that sense, execution management is not an optional layer of infrastructure, but a necessary one.