.png)
Trading systems integration is key to operational efficiency and profitability in financial markets and the crypto space is no exception. This article will explore three key components of trading infrastructure: Order Management Systems (OMS), Execution Management Systems (EMS) and the hybrid Order Execution Management Systems (OEMS). Each of these systems serves a different purpose in the trading process for different needs within financial institutions from portfolio management to trade execution.
Order Management Systems (OMS) are designed to manage the life of an order, to execute trades according to a predetermined strategy. They track orders from inception to settlement, providing portfolio managers with information on cash positions, asset allocation and compliance with investment mandates. Execution Management Systems (EMS) are focused on the actual execution of trades in the market, providing traders with tools to route orders and achieve best execution at the best price. Combining these systems into an Order Execution Management System (OEMS) brings together the strengths of OMS and EMS, simplifying workflows and reducing operational risk from fragmented trading processes.
By using these technologies firms can improve their operational efficiency and get a competitive advantage in today’s fast paced trading environment. This article will look at the definitions, differences, benefits and use cases for each system.
What is an Order Management System?
An Order Management System (OMS) is a trading infrastructure component that automates and integrates all the tasks involved in the life of a trade order. From routing the order to an exchange and finding the counterparty to reconciling transactions in accounting systems, an OMS ensures seamless execution across all these functions. By connecting the different parts of a market’s infrastructure, OMSs are the backbone of trading operations, providing liquidity and operational certainty.
OMSs are versatile because they serve different market participants. Individual traders use OMSs to buy or sell, broker-dealers use them to offer trading to their clients, exchanges use them to manage liquidity and market makers use them to track positions across multiple venues and arbitrage opportunities. In crypto markets OMSs do the same as in traditional financial markets but with added functionality for the digital asset space such as wallet integrations and custody solutions.
History of Order Management Systems
Order Management Systems were born out of the inefficiencies of how trading firms used to handle data and processes across their front, middle and back office. Before OMSs, these departments were separate, with different systems and siloed workflows. This lack of integration caused operational bottlenecks, preventing firms from executing trades in fast moving markets. For example, trade clearing was sequential, meaning traders had to wait for backlogs to clear before they could act on market opportunities – a costly inefficiency in fast markets.
OMSs were created to address these inefficiencies by centralising and simplifying workflows. While the simplicity of an OMS interface hides its complexity, the system connects to a wide range of stakeholders from trading exchanges and institutional investors to customers.
On Wall Street OMSs used to bridge the buy-side (portfolio and fund managers focused on building high performing investment portfolios) and the sell-side (investment banks and their trading floors). Protocols like the Financial Information eXchange (FIX) and WebSocket established a standard data exchange, allowing for fast and synchronous trade execution across multiple platforms. Over time OMS software has added advanced analytics, real-time trading data and back-testing tools for trading strategies.
Today an OMS is more than just a nice to have; it’s a competitive advantage. By allowing firms to trade fast and accurately an OMS helps trading firms to take advantage of market opportunities and react to market dynamics, in traditional or digital asset markets.
Advantages of an OMS in crypto trading
Order Management Systems (OMS) are key to modern trading by providing a set of benefits that improve efficiency, accuracy and decision making for traders, brokers and asset managers. Here are the main benefits of using OMS in the crypto market:
Faster and More Scalable
An OMS automates the mundane tasks of order placement, execution and reporting, so traders and brokers can focus on strategy rather than operations.
The ability to handle large volumes and connect to multiple venues means firms can scale without performance degradation, a must for institutional traders managing high frequency trades or diversified portfolios.
Better Trade Management
Real time tracking lets traders see the status of their orders so they can adjust quickly to changing market conditions.
An OMS supports multiple order types including complex strategies like stop-loss and algorithmic orders, giving traders more ways to fine tune their trading.
Risk Management
By doing pre-trade checks OMSs ensure trades comply with position limits or portfolio restrictions, reducing the risk of unauthorized or over-trading.
With real time data on trades, positions and market movements traders can manage their risk exposure in line with institutional risk management policies.
Compliance and Reporting
OMSs make compliance easier by generating audit trails, regulatory reports and financial disclosures automatically. So firms can meet their regulatory requirements with less manual effort.
The detailed transaction records kept by OMSs make tracking and auditing trades easy, for both compliance teams and external auditors.
Fewer Errors and Operational Costs
Automating trade execution and reporting workflows reduces human error, such as incorrect trade entry or misplaced orders. So there’s less chance of errors throughout the trading process.
By streamlining workflows and reducing manual work OMSs help firms cut operational costs and avoid financial losses from trade mistakes.
Trading Strategies
Advanced OMS platforms support algo trading so traders can execute pre-defined strategies based on price, volume or time.
An OMS can be a single platform to manage multiple asset classes, such as crypto, stocks and derivatives, so cross-asset trading and portfolio diversification is easier.
Real Time Analytics for Better Decision Making
OMSs provide actionable insights through real time analytics so traders can optimise strategies and adapt to market changes.
Portfolio managers can see multiple portfolios, track performance metrics and adjust positions based on live market data to get better portfolio outcomes.
Broker Management
For brokers an OMS makes managing large volumes of client orders easy, so execution and allocation is accurate and efficient across client portfolios.
Customisable reporting means brokers can generate detailed execution and performance reports for their clients, so clients are more transparent and trusting.
Access to Liquidity and Markets
OMSs give global access by connecting to multiple venues, so firms can trade across multiple markets. More liquidity and more reach.
Order Management Systems are here to stay for traders and institutions in the rapidly changing crypto landscape. Whether it’s faster, fewer errors or more advanced strategies OMSs give market participants an edge.
When choosing a crypto OMS
Until crypto market infrastructure is fully built out popular OMSs won’t add crypto trading to their services. If you’re looking at OMSs for the crypto market you should consider:
-
Latency: Crypto can be more volatile than traditional markets, and most trading venues utilize cloud-based infrastructure. So a trade order management system for cryptocurrencies needs to keep up with price changes and show them with minimal latency so traders can react to market volatility.
-
Exchanges: There are over 700 crypto exchanges around the world today according to Coinmarketcap.. These exchanges present an arbitrage opportunity for traders as prices can differ across platforms. So a good crypto OMS should connect to the most liquid and well known exchanges for crypto traders to execute their arbitrage strategies.
-
Regulatory Compliance: OMS functionality needs to allow crypto traders to be compliant with crypto regulations in their region; so the OMS should be able to generate comprehensive trading reports and other regulatory documents in time.
A multi-actor case for Order Management Systems
Order Management Systems (OMS) are at the heart of the financial markets serving the needs of traders, brokers and asset managers. The flexibility of an OMS lies in its ability to simplify operations, improve trade execution and manage risk across multiple actors. Here’s how OMS is essential for each:
For Traders
An OMS allows traders to trade across multiple exchanges and asset classes, with real time market data to make decisions fast. This is especially important during market volatility where speed and accuracy matters.
Algorithmic and high frequency trading strategies also benefit from OMS as the system automates complex order placement, minimising manual intervention and errors. Traders can see their trades in real time, so can execute accurately and adjust or cancel when market conditions change.
For Brokers
Brokers use OMS to manage large volumes of client orders across multiple markets and asset types. The system ensures allocation and settlement so brokers can manage multiple client portfolios without delay or error.
Compliance is a big part of their business so brokers benefit from OMS automation in reporting and trade management. OMS reduces the risk of non-compliance so brokers avoid penalties. And the faster and more accurate execution helps brokers deliver better service and build stronger client relationships.
For Asset Managers
Asset managers use OMS to manage and execute trades across multiple portfolios from one single interface. This gives them real time visibility into order status, portfolio performance and market dynamics so they can make informed and timely decisions.
An OMS simplifies trade allocation so assets are distributed as per client mandates. And its integration with portfolio management tools gives them insights into risk exposure and market volatility so they can manage risk proactively. With detailed reports on trade execution, compliance and portfolio performance asset managers can track, analyse and optimise their strategies.
By serving the needs of traders, brokers and asset managers Order Management Systems are at the heart of financial markets, managing trades, compliance and operations.
What is an Execution Management System (EMS)?
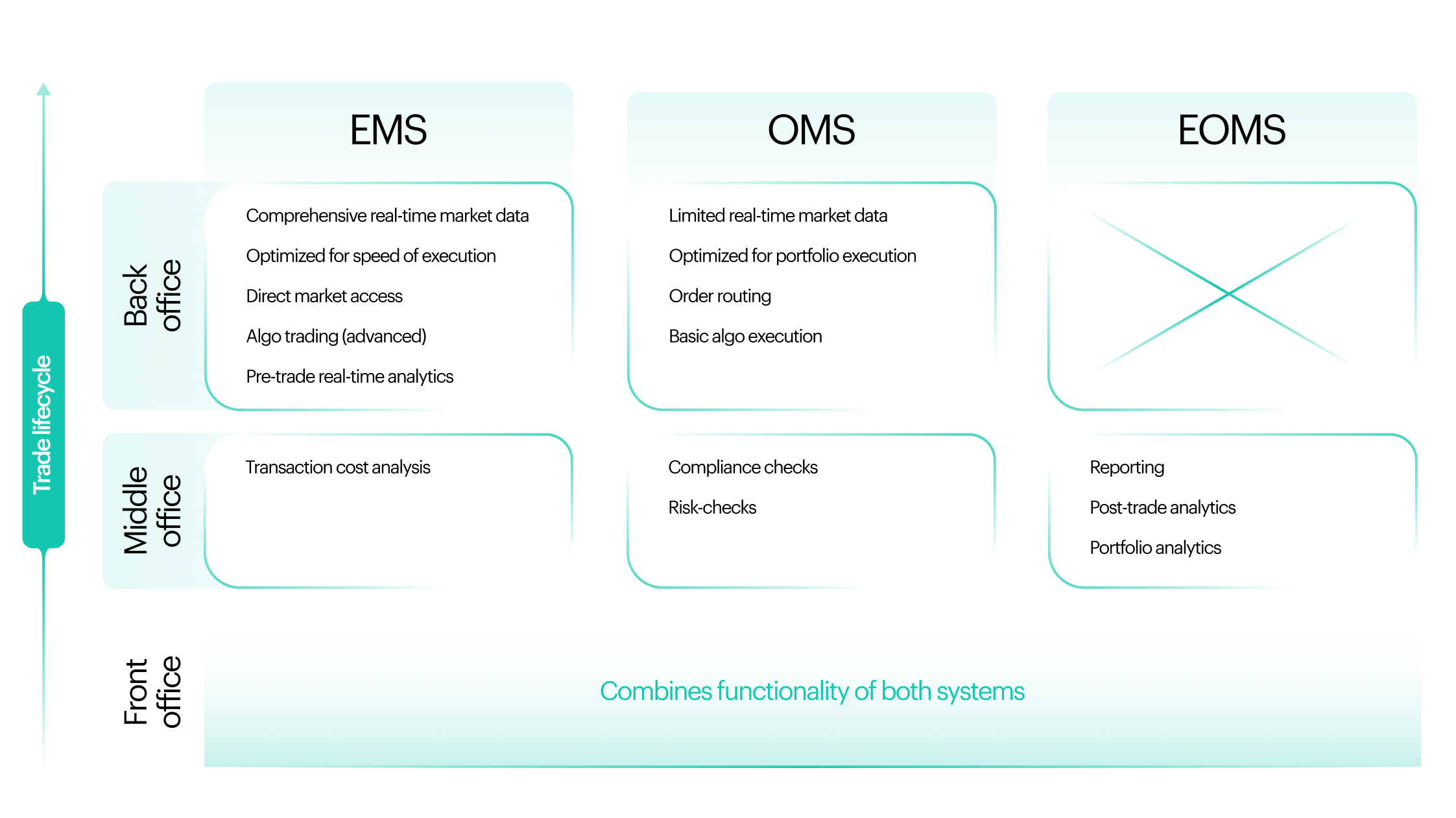
An Execution Management System (EMS) is a trading platform designed for the buy side. It allows traders to trade efficiently by providing real time market data, execution options, liquidity management and transaction cost analysis. The aim of an EMS is to optimize trade execution, improve trading strategies and reduce overall trading costs.
EMS platforms may support multiple asset classes but are often focused on specific markets such as equities, fixed income or crypto. This is because each asset class has its own unique trading requirements. A fixed income trading system requires completely different features and integrations than a crypto focused EMS.
Execution Management System providers offer different solutions, some a single multi-asset EMS and others separate platforms for each asset class. This means traders can choose a solution that fits their specific trading needs whether they are focused on one market or multi-asset trading.
Features of Execution Management Systems
Advanced Execution Options
One of the key features of an EMS is the range of advanced execution options. Beyond basic market or limit orders traders can use complex order types such as conditional orders, multi-leg orders and list trading. These tools allow traders to fine tune their strategies and optimize execution for complex trade scenarios.
Liquidity Management
A key part of an EMS is the ability to centralise access to liquidity across multiple venues. By aggregating liquidity data the system allows traders to see opportunities at different venues so they can make informed decisions on where to execute trades. Some EMS platforms also allow traders to split orders into smaller segments to be executed across multiple venues to improve execution and reduce market impact.
Real-Time Market Data
EMS platforms provide real time market data so traders have up to the minute information on prices, volumes and liquidity. This is essential for making informed decisions and responding to market changes.
Transaction Cost Analysis (TCA)
Many EMS platforms have Transaction Cost Analysis (TCA) tools. These tools allow traders to measure the cost of trade execution, measure execution quality and identify areas for improvement. TCA helps traders refine their strategies, manage costs and get better trading outcomes.
By combining these features EMS are essential tools for traders to be more efficient, optimize their strategies and get better execution in fast changing markets.
Order and Execution Management Systems (OEMS): A Hybrid Solution
Order Execution Management Systems (OEMS) are the combination of Order Management Systems (OMS) and Execution Management Systems (EMS), streamlining workflows across the front and middle/back office. This hybrid approach combines the best of both systems, for efficient order routing, trade allocation and compliance checks and overall trading process.
OMS and EMS integration gives traders direct access to order information within one platform so they can see and act on orders earlier in the trading process. This seamless connection means smoother trade execution and more operational efficiency.
One of the benefits of OEMS is its flexibility. The best OEMS solutions are cross asset and can support any EMS while maintaining order and portfolio management. But the lines between buy-side trading technologies such as OMS, EMS and Portfolio Management Systems (PMS) are blurred as many vendors offer overlapping functionality.
OEMS can handle a wide range of tasks such as order entry and execution across multiple liquidity providers, analytics, market data streaming, charting and transaction cost analysis (TCA). They can be accessed manually by traders and programmatically through APIs like FIX.
In the crypto markets OEMS play a key role in connectivity management. Unlike traditional financial markets like FX where FIX protocols and infrastructure are established and consistent, crypto liquidity providers have different connectivity requirements. The lack of standardisation adds complexity and OEMS need to adapt and manage multiple connection protocols. As a result crypto OEMS have to handle not only trading functionality but also the challenge of managing dynamic connectivity across a fragmented market.


.png)























